Interest rates play a crucial role in the world of business loans, influencing borrowing costs and ultimately impacting the financial decisions of companies. Understanding how interest rates affect business loans is essential for entrepreneurs and business owners seeking financing to grow their operations or navigate through challenging times. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this relationship to shed light on the dynamics at play.
The Basics of Interest Rates and Business Loans
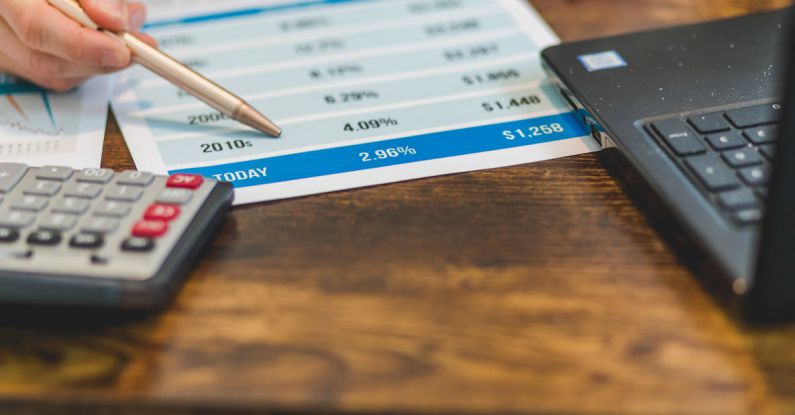
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money and are determined by various factors, including economic conditions, inflation rates, central bank policies, and market demand. When it comes to business loans, interest rates can significantly influence the overall cost of borrowing for companies. Lenders charge interest on loans as a way to earn a return on their capital and compensate for the risk associated with lending money.
Impact on Borrowing Costs
The most direct impact of interest rates on business loans is on borrowing costs. When interest rates are low, businesses can access financing at more affordable rates, reducing the overall cost of capital. This can be particularly advantageous for small businesses and startups with limited resources, as lower borrowing costs make it easier to invest in growth opportunities or manage cash flow.
Conversely, when interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase, making it more expensive for businesses to take out loans. Higher interest rates can squeeze profit margins and put pressure on cash flow, especially for businesses with variable-rate loans that are tied to market interest rates. In such scenarios, companies may need to reassess their borrowing needs and explore alternative financing options to mitigate the impact of rising interest rates.
Effect on Investment Decisions
Fluctuations in interest rates can also influence the investment decisions of businesses. When interest rates are low, companies are more likely to borrow money to fund expansion projects, invest in new equipment, or hire additional employees. Low borrowing costs make it attractive for businesses to take on debt to finance growth initiatives and capitalize on opportunities in the market.
On the other hand, higher interest rates can lead to a decrease in investment spending as businesses become more cautious about taking on additional debt. When borrowing costs rise, companies may prioritize paying down existing debt or conserving cash rather than investing in new projects. This can slow down economic activity and dampen overall business growth, impacting both individual companies and the broader economy.
Managing Interest Rate Risk
Given the impact of interest rates on business loans, it is essential for companies to manage interest rate risk effectively. One way to mitigate the effects of interest rate fluctuations is to diversify financing sources and consider a mix of fixed-rate and variable-rate loans. Fixed-rate loans provide certainty in interest payments, as the rate remains constant throughout the term of the loan, while variable-rate loans offer flexibility but expose borrowers to fluctuations in interest rates.
Businesses can also explore hedging strategies, such as interest rate swaps or options, to protect against adverse movements in interest rates. These financial instruments can help companies lock in favorable rates or limit exposure to rising interest costs, providing a level of predictability in financing expenses.
In conclusion,
Navigating the complex relationship between interest rates and business loans is a critical aspect of financial management for companies of all sizes. Understanding how interest rate movements can impact borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall financial health is key to making informed financing choices and positioning businesses for long-term success. By staying informed about market trends, exploring different loan options, and implementing risk management strategies, businesses can effectively navigate the challenges posed by changing interest rates and seize opportunities for growth and expansion.